
Analysis of the Curio Exploit
Learn how Curio was exploited, which resulted in a loss of approximately $16 million.
Youtube Video
Playing the video that you've selected below in an iframe

On December 13, 2022, Elastic Swap was exploited due to price manipulation. Total loss: $854,000.
On December 13, 2022, Elastic Swap was exploited due to price manipulation causing a total loss of approximately $854,000.
Elastic Swap operates on the Avalanche C-Chain platform, and is an automated market maker focused on elastic supply tokens like $AMPL.
The root cause of the vulnerability is due to the usage of two different accounting system which led to inconsistent calculation for adding and removing liquidity in contracts.
Step 1:
We tried to analyse the attack transaction carried out by the exploiter.
Step 2:
The exchange contract used a constant K value algorithm to add liquidity; however, to remove liquidity, it calculates the tokens to return using the token-balance in the current pool and reduces the internal accounting reserves.

Elastic Swap Smart Contract Screenshot, Courtesy of Etherscan.
Step 3:
Due to such design, the attacker first added liquidity, before transferring some $USDC.e directly to TIC-USDC pool.
Step 4:
The amount of $USDC.e to be transferred to the attacker is multiplied by the number of LP tokens, then the attacker removed this liquidity to make a profit.
Step 5:
This attacker made a profit of approximately 22,454 $AVAX worth $290,328, and subsequently transferred them to another address.
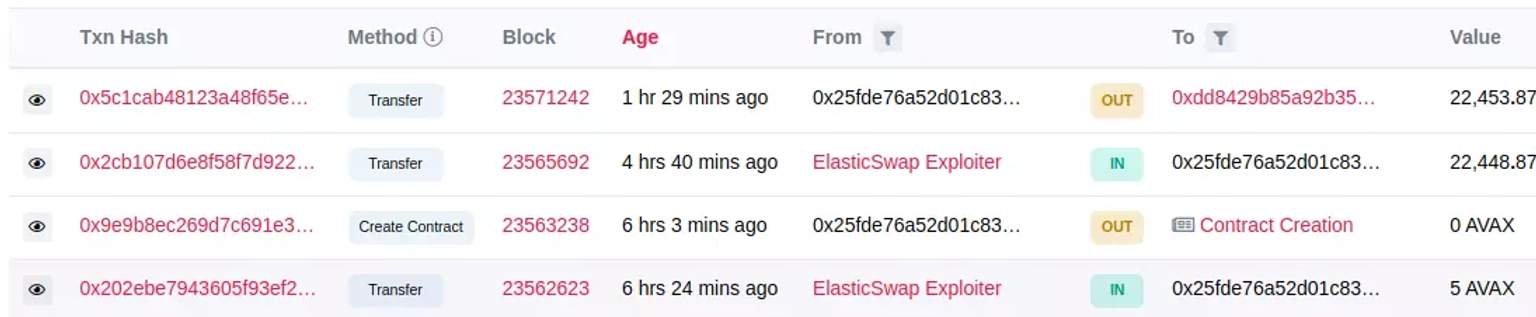
Elastic Swap Hacker Transaction Screenshot. Courtesy of Snowtrace.
Step 6:
The AMPL-USDC pool of ElasticSwap on Ethereum was also compromised using the same method.
Step 7:
The attack was front run by a MEV bot, and the attack transaction carried out by the exploiter can be viewed here.
Step 8:
The attacker made a profit of roughly 445 $ETH worth around $564,000, which remains in the attacker's account.
The team published a Tweet stating that they have been compromised, and have asked users to remove their liquidity.
The attack also caused the project's TIC token to drop by more than 77% of its value, and was found to be trading at $1.05 at the time of this writing.
In order to prevent such attacks, it is of paramount importance to rigorously assess potential attack vectors and ensure the security of smart contracts before deployment. This includes conducting comprehensive audits or subjecting contracts to stringent tests within simulated environments to identify potential vulnerabilities.
The impact of this attack could have been notably mitigated had Elastic Swap been equipped with a dedicated cover pool within the Neptune Mutual marketplace. While standard terms and conditions already offer coverage for a range of DeFi attacks, including smart contract vulnerabilities, exceptions can be made in certain cases.
Users who purchase our parametric cover policies are exempt from the need to furnish loss evidence to access payouts. Payouts can be swiftly claimed once an incident is resolved through the governance system.
Moreover, recognizing that smart contract audits alone may not suffice due to the diverse range of attack vectors, Neptune Mutual's security team extends its assessment to encompass various domains, including DNS and web-based security, smart contract evaluations, and both frontend and backend security.
In conclusion, the Elastic Swap exploit emphasizes the significance of proactive security measures within the DeFi landscape. Neptune Mutual emerges as a vital ally in this endeavor, offering a means to curtail the impact of such vulnerabilities and providing a pathway to enhanced security and recovery.
Reference Source BlockSec, PeckShield