
Understanding the Grand Base Exploit
Learn how Grand Base was exploited, resulting in a loss of assets worth $2.5 million.
Youtube Video
Playing the video that you've selected below in an iframe

Learn how Platypus Finance was exploited via flash loan attack leading to a loss of $9 million.
On February 16, 2023, Platypus was exploited via a flash loan attack, resulting in the total loss of approximately $9 million.
Platypus Finance is a single-sided Automatic Market Maker for stablecoins built on the Avalanche network designed to optimize capital efficiency.
The vulnerability occurred due to a logic error in the USP solvency check mechanism of their contract holding the collateral.
Step 1:
We attempted to analyze one of the attack transactions executed by the exploiter.
Step 2:
The flaw existed in the implementation of MasterPlatypusV4 contract, in which the emergencyWithdraw function incorrectly evaluated the insolvency before the removal of the collateral.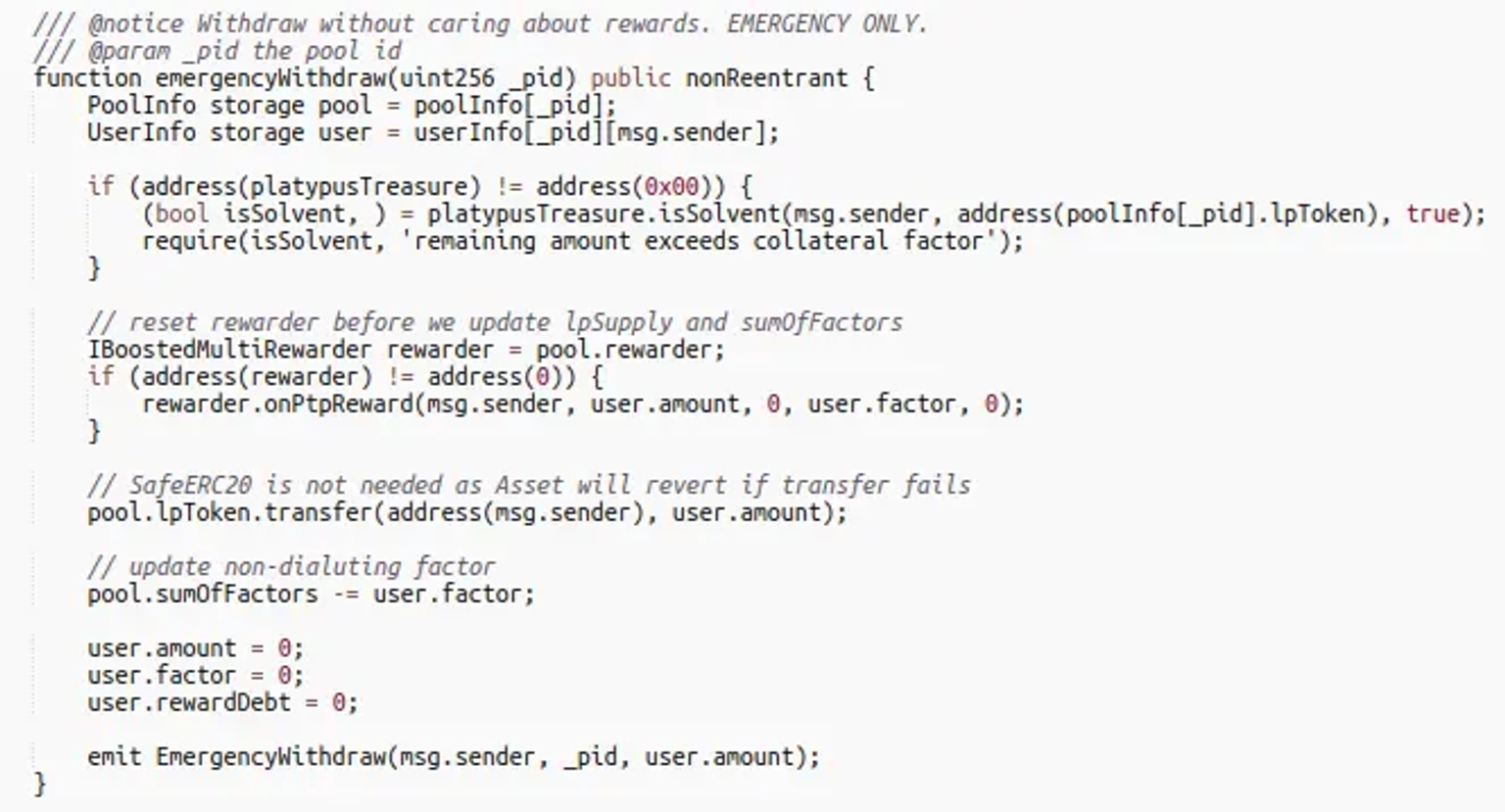
Step 3:
The exploiter initially took a flash loan of 44 million $USDC from AAVE, and deposited them to Platypus Finance Pool there by minting ~ 44 million LP-USDC.
Step 4:
The attacker then deposited 44 million LP-USDC to MasterPlatypusV4 as collateral in order to borrow 41.7 million USP from PlatypusTreasury.
Step 5:
This led to an insolvent debt position causing an emergency withdraw of 44 million LP-USDC from MasterPlatypusV4 contract.
Step 6:
They then withdrew earlier deposited 44 million $USDC from Platypus Finance Pool, and swapped 8.75 million USP, which is the Platypus’s stablecoin, to multiple assets consisting of $USDC, $USDC.e, $USDT, $USDT.e, $BUSD, and $DAI.
Step 7:
The swapped assets were kept for profits, while the borrowed flash loan was repaid back to AAVE.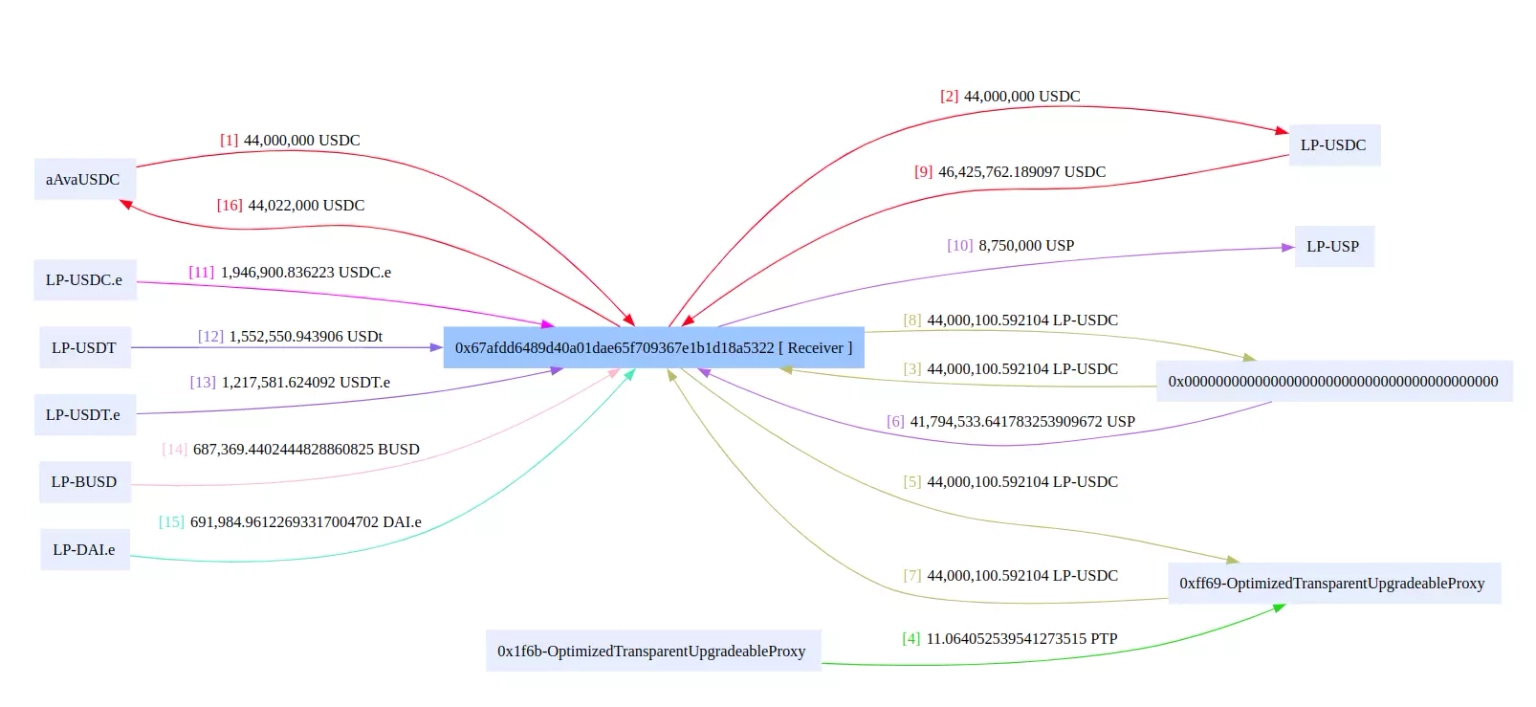
Funds Flow of Platypus’s Attack Transaction. Courtesy of BlockSec
Step 8:
At the time of this writing, the contract deployed by the attacker holds all the stolen assets, which are worth approximately $8.5 million.
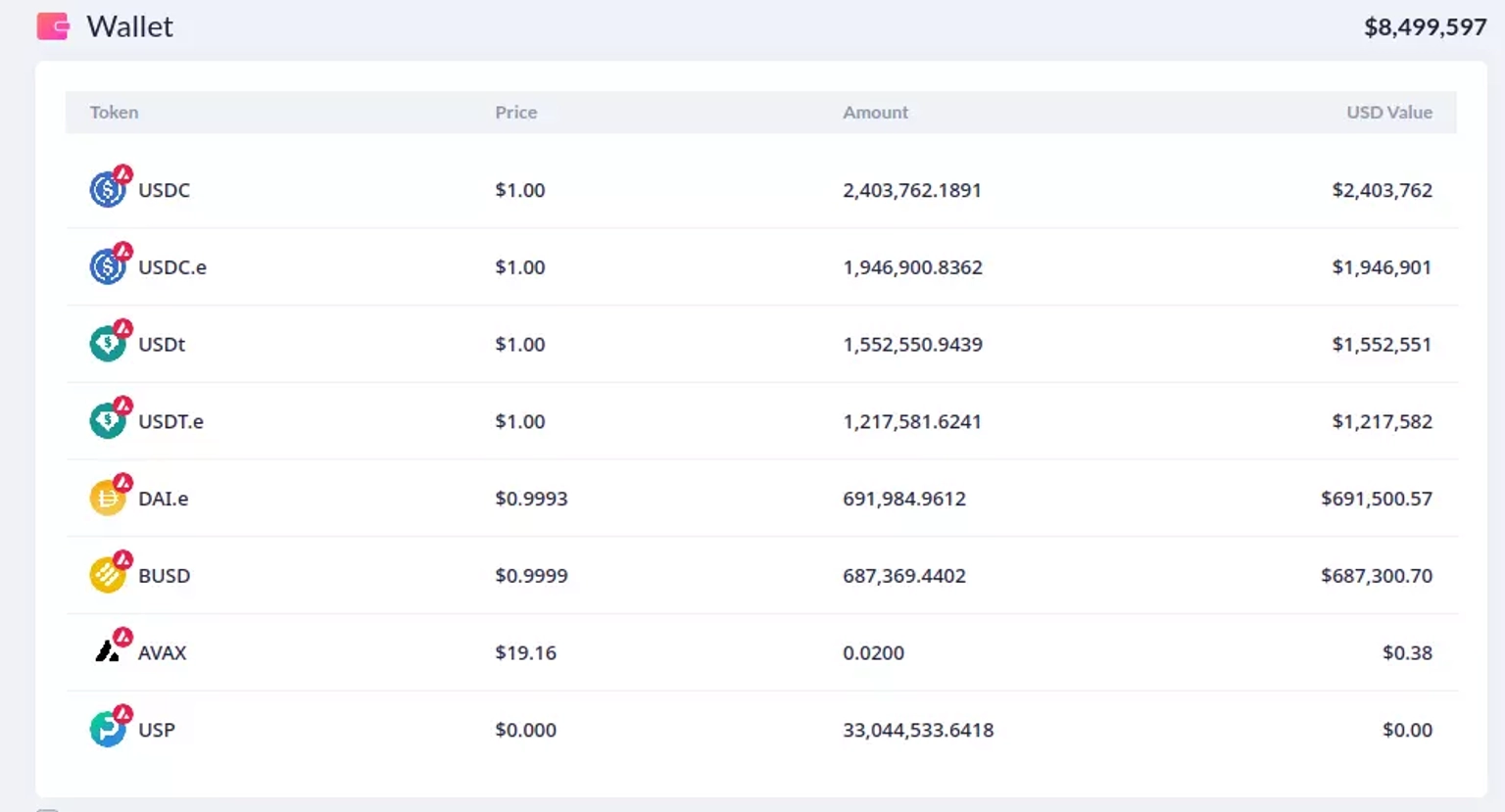
Step 9:
The profits from the second attack transaction were $172,064, while yet another attack transaction netted them approximately $380,000.
The team announced the occurrence of the incident and its root cause on Twitter. They stated that the hacked funds originated from the main pool, while funds in the other pools remained unaffected.
According to the team, they are collaborating with third parties, including Binance, Tether, and Circle. The stolen USDT funds have been frozen, and Tether has blacklisted the attacker’s address.
They further mentioned that they are exploring options for compensation and reimbursement for affected investors.
The team later reported that they were able to recover approximately 2.4 million USDC from the attacker's contract, with the assistance of the BlockSec team.
The unfortunate exploitation of Platypus Finance through a flash loan attack underscores the intricate challenges and nuances present in the world of DeFi. As we dissect the steps leading up to the attack, from the flawed solvency check mechanism in the USP solvency check to the series of transactions made by the exploiter, it’s evident that we are not just dealing with simple oversights. These are complex issues that stem from subtle logic errors that, when combined with large capital flows, can have devastating consequences.
The heart of this issue lies in the faulty implementation of the MasterPlatypusV4 contract. A mistake in the emergencyWithdraw function turned out to be a costly one. Proper contract testing—ranging from unit testing to integration testing to functional testing—could have brought this oversight to light before deployment. The significance of these tests lies in their ability to rigorously challenge every facet of a contract, particularly when millions of dollars are at stake.
Moreover, the increasing sophistication of attacks and the rapid innovation in DeFi mandate the use of formal verification tools. These tools serve as the last line of defense, ensuring that the contract not only functions but functions precisely as intended, leaving no room for malicious exploits.
However, while prevention is vital, protection is equally paramount. And this is where Neptune Mutual steps in.
The aftermath of this attack could have been significantly cushioned had Platypus Finance established a dedicated cover pool with Neptune Mutual. Our parametric policies are tailored for unforeseen events like these. These policies offer users solace and a buffer against financial shocks. Under our system, the process of filing claims becomes uncomplicated. Affected users, instead of delving into the tedious task of providing loss evidence, can readily claim payouts once an incident is determined and resolved. At the moment, our marketplace is available on two popular blockchain networks, Ethereum, and Arbitrum.
But Neptune Mutual's intervention doesn’t just stop at providing coverage policies. We take pride in our proactive stance towards security. Our seasoned security team is adept at performing extensive platform evaluations. These range from essential DNS and web-based evaluations to advanced backend security audits. By partnering with us, platforms like Platypus Finance could leverage our expertise to preemptively identify and fortify against potential vulnerabilities.